1. Description and Method of Calculation of Indicators
* Intentional lethal violence rate
This indicator calculates the intentional violent deaths. It considers the number of deaths per 100,000 inhabitants and includes the following criminal occurrences: murder; death followed by injury of the victim, and robbery followed by death (aggravated burglary).
Calculation method:

Information available for the years: 2009 and 2010.
* Murder rate
This indicator calculates all cases of injury followed by death (voluntary offense to body integrity or health of others, resulting in unintentional death of the victim) per 100,000 inhabitants. The source of these data is the Civil Judicial Police.
Calculation method:

Information available for the years: 2009 and 2010.
* Aggravated assault killings rate
This indicator calculates all cases of injury followed by death (voluntary offense to body integrity or health of others, resulting in unintentional death of the victim) per 100,000 inhabitants. The source of these data is the Civil Judicial Police.
Calculation method:

Information available for the years: 2009 and 2010.
* Robbery followed by death rate (aggravated burglary)
This indicator calculates all cases of theft which violence used resulted in the death of the victim per 100,000 inhabitants. This includes any type of robbery resulting in death (a passerby, at residence, at financial institution, vehicle, load, in the shop, etc.). The source of these data is the Civil Judicial Police.
Calculation method:
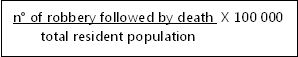
Information available for the years: 2009 and 2010.
* Property crimes rate - except vehicles
This indicator calculates property crimes with or without use of violence and/or threat. It considers the number of criminal incidents per 100,000 inhabitants and includes theft (subtracting other people using violence and/or threat) and theft (subtracting other people who did not use violence and/or threat).
Calculation method:

Information available for the years: 2009 and 2010.
* Robberies rate - except vehicles
This indicator accounts for total occurrences of theft per 100,000 inhabitants. The data source is the Civil Judicial Police. The burglary rate aggregates all kinds in a total indicator. Despite not having the kinds of thefts in a disaggregated form, we will define each one of them according to technical specification:
a) Passerby robbery: is the total of all robberies against non-motorized individuals, practiced on a public road or public area, whatever may have been the object or subtracted value (money, cell phone, jewelry, bicycle, documents, weapons etc.);
b) Burglary to residence: are accounted all robberies committed inside private residence, building, or private residential condominium, whatever may have been the type object or subtracted value (money, cell phone, jewelry, appliances, bicycle, documents, weapons etc.).
c) Theft in commercial establishment: sum of all robberies committed within commercial establishments or supplier of commercial services, with public access: any kind shop, restaurant, bar, hotel, pharmacy, clinic, mall, supermarket, lottery house, post office, gas station, sales outlet for agricultural supplies, cinema, theater, house parties, theme park etc. where harmed by the theft are individuals or entities. This does not include thefts committed inside private establishments or establishments with restricted access (clubs, condominiums, factories, warehouses wholesalers, farms etc.). It does not include either private vehicle theft or vehicle cargo carriers or carriers of values (armored car) parked in a commercial establishment area.
d) Theft with restriction of freedom of the victim: this item adds up all instances of theft in which the actor, to consummate the crime, restricted freedom of the victim, keeping the victim in their power through violence or serious threat. This includes the popularly known crime as “shanghaiing,” provided it has not involved or has not evolved to a request, to third parties, of ransom or other benefits as a condition for the release of the victim.
e) Other kinds of theft: is the sum of all other occurrences of theft not recorded in any of the previous categories specified above. For example, vehicle parts theft, theft within private vehicle or taxi, robbery within educational institution, robbery inside government agency or theft to non-financial public agency, robbery to industrial establishment, robbery to farm or other rural property, theft inside aircraft or vessel (except if subtracted along with the load); robbery to non-commercial trailer, and so on.
Calculation method:

Information available for the years: 2009 and 2010.
* Thefts rate - except vehicles
This indicator accounts for the total recorded thefts incidents per 100,000 inhabitants. The data source is the Civil Judicial Police. The thefts rate aggregates all types in a total indicator. Despite not having the types of thefts in a disaggregated form, has been defined each one as the technical specification:
a) Theft of cargo: in this item are summed all occurrences of theft of cargo, including those in which the cargo vehicle was subtracted along with the load either configure simple thefts, qualified, aggravated or common thing related. Thefts are accounted here (including withdrawals) of all types of cargo with commercial value (food, beverages, fuel, machinery, building materials, appliances or electronics, livestock, chemicals, industrial etc.), transported in any vehicle, whether land, air and rail. It's not accounted here thefts of fiduciary values transported in vehicles carrying values (armored car).
b) Passerby theft: is the sum of all the individual thefts to a person non-motorized, practiced in public path or public area, whatever may have been the object or subtracted value (money, cell phone, jewelry, documents, weapons etc). Not included here thefts within public transport nor private vehicle or taxi.
c) Theft in residence: here are summed all simple robberies, qualified, aggravated or of common things practiced within private residence, building, or closed residential condominium set, whatever may have been the object type or subtracted value (money, cell phone, jewelry, appliances, bicycle, documents, weapons etc.). Not accounted here are vehicles thefts, loaded or unloaded, parked inside residential complexes or closed condominiums.
d) Other thefts: is the sum of all other occurrences of simple thefts, qualified, aggravated or of common things not accounted in any of the categories above. For example, theft inside private vehicle, taxi or public transportation; theft within office or public agency, theft within/of financial institution; cattle-rustling (stealing livestock except cattle transported in cargo vehicle); robbery in a commercial establishment or service; theft in religious establishment; theft in school; theft with burglary (except if of vehicle or residence); robbery of/at ATM, robbery in/of transportation values vehicle (armored car); gun theft (except if the victim is a pedestrian or bystander); theft of telephone cable; theft of electricity, theft of aircraft, train or boat, vehicle license plate or traffic signs, and so on.
Calculation method:

Information available for the years: 2009 and 2010.
* Women's homicide rate (*)
The indicator calculates the intentional violent deaths against women. It considers the number of deaths of females per 100,000 inhabitants (of that demographic group) and includes deaths due to intentional aggression of others, using any means to cause damage, injury or death of the victim.
This indicator is created from the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10) from the Ministry of Health on “external causes of morbidity and mortality” and results from the sum of the subcategories of assault (X85 to Y09). The deaths of women are accounted by the sum of these categories per 100,000 inhabitants (of that demographic group). Among deaths due to external causes for assault it been found death caused by firearms, drill blunt object, drowning, and burns, among others.
For the record of spatial location of death, the place of residence has been used because it is considered closer to where the violence was provoked. We know that in some cases the incident differs from the place of the death, as is the case with individuals taken to hospitals located in other cities.
Calculation method:

Information available for the years: 2009 and 2010.
* Homicide of children and adolescents rate (0-18 years) (*)
The indicator estimates the intentional violent deaths committed against children and adolescents. This makes it possible to estimate the lethal violence practiced against specific age groups most vulnerable or the risk of homicides of children and adolescents. The number of deaths of children (0 to 9 years old) and adolescents (10 to 18 years old) per 100,000 inhabitants from 0 to 18 years old have been considered, and include deaths due to intentional assault from others who use any means to damage, injure or kill the victim. The data source used is the DATASUS and the Health Department of the State of Mato Grosso.
Calculation method:

Information available for the years: 2009 and 2010.
* Homicide of children rate (0-9 years) (*)
This indicator calculates the deaths for assault of children aged 0 to 9 years, resulting from external causes (categories X85 to Y09 from External causes of morbidity and mortality in the CID-10 from the Ministry of Health) per 100,000 inhabitants (age group). Among the deaths due to external causes for assault, it is found death caused by firearms, drill blunt object, drowning, and burning, among others. For the record of spatial location of the death, place of residence has been used.

Information available for the years: 2009 and 2010.
* Rate of adolescent homicide (10 to 18) (*)
This indicator calculates the deaths for assault of pre-adolescents from 10 to 18 years old, resulting from external causes (categories X85 to Y09 from External causes of morbidity and mortality in the CID-10 from the Ministry of Health) per 100,000 inhabitants (age group). Among the deaths due to external causes for assault, it is found death caused by firearms, drill blunt object, drowning, and burning, among others. For the record of spatial location of the death, place of residence has been used.

Information available for the years: 2009 and 2010.
* Homicide of young people rate 19-29 years (*)
This indicator would be similar to the previous one in order to estimate the intentional violent deaths practiced against particular age groups that are most vulnerable. However, it considers the number of deaths of young people (from 19 to 29 years old), per 100 000 inhabitants from 19 to 29 years and includes deaths due to intentional aggression of others, using any means to cause damage, injuries or the victim's death. The data source used is the DATASUS and Department of Health from the State of Mato Grosso.
Calculation method:

Information available for the years: 2009 and 2010.
* Homicides of youth rate 19 and 24 years
This indicator considers the number of deaths of young people (from 19 to 24 years old) per 100,000 inhabitants in this age group and includes the deaths due to intentional aggression of others, using any means to cause damage, injury or death to the victim. The data source used is the DATASUS and Department of Health from the state of Mato Grosso.
Calculation method:

Information available for the years: 2009 and 2010.
* Homicides of youth rate 25 to 29 years (*)
This indicator would be similar to the previous one in order to estimate the intentional violent deaths practiced against particular age groups that are most vulnerable. However, it considers the number of young people (from 25 to 29 years old), per 100,000 inhabitants in this age group and includes deaths due to intentional aggression of others, using any means to cause damage, injury or death of the victim. The data source used is the DATASUS and Department of Health from the state of Mato Grosso.

Information available for the years: 2009 and 2010.
(*) See next section which deals with the calculation methodology for the estimation of homicide.



